
I am currently researching into artists from Ilford. (Ilford is one answer to where I’m from)
Gillian Wise was a British visual artist born in Ilford. She was part of the English Constructivist movement of the 1950s before becoming a key member of the Systems group.
“Her work follows the principles of experimentation and reduction to elemental units (line, colour, and plane). Her structures play on the effects of the geometry of light and industrial materials, as well as contrasts between transparency and the primary colours.” – aware

Gillian Wise was born in Ilford in 1936. She grew up in Ilford until leaving the area to study at 18 in Wimbledon. She exhibited as part of the British constructivists and became their youngest member in 1961. She challenged the predominance of American modernism at the time and then continuously throughout her career. She clearly understood art and artistic production to be an overtly political matter and spoke often about the CIA intervention in Cold War cultural production.
From her book, Low Frequency:
“There artists of all stripes and their nascent agents had to be American to get the full treatment of nurture and sponsorship since that is what policy demanded. Policy from Washington. Out of this was born the Abstract Expressionist group… the two names which have been retained as most representing that moment are Pollock and Rothko, although the latter was trying for a stylistic variant. While Pollock reflects some early Alexander Rodchenko (one of the original and prolific members of the Russian Constructivist movement) experiments, Rothko’s attempt at mysticism, à la Malevich, is a very thin affair.”
Her work was overtly political and she herself was an avowed Leftist who won a British Council scholarship to research Russian constructivism in 1969. She travelled to Leningrad, exhibited in Helsinki and joined the Systems group, a collection of Marxist artists who successfully produced and showed work throughout the 70s.
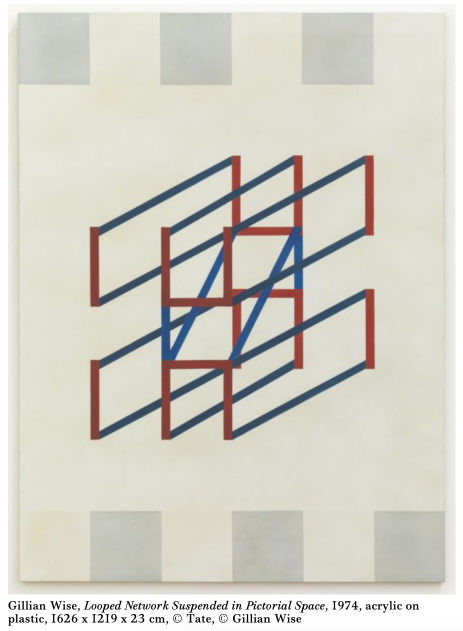
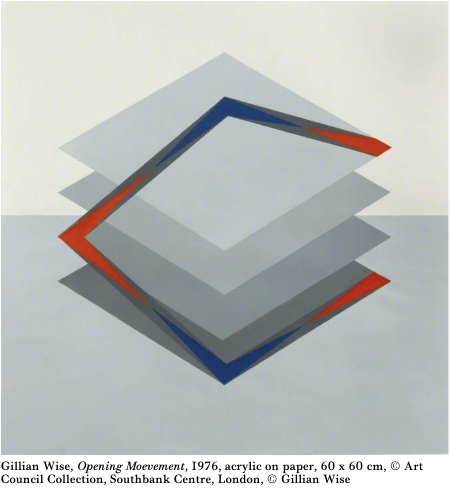
Gillian Wise was the only British artist to create work for the opening of the Barbican centre in 1982. Her work, the Alice Walls, inspired by the Russian avant-garde, remained entirely uncredited until 2014. She referenced it as, “a dark episode in the annals of support for national artists and, of course, women.”
The history of this Ilford-born artist gives so much rich context to the sidelining of genuinely Leftist and Marxist positions throughout the Cold War. It also references the definite and unacceptable misogyny of the mainstream British art establishment who have since begun to rewrite their silence around Gillian Wise with her inclusion in a variety of shows.
While on the surface it seems that Ilford plays a limited or invisible role in the artists history, one striking historical coincidence keeps me wondering.
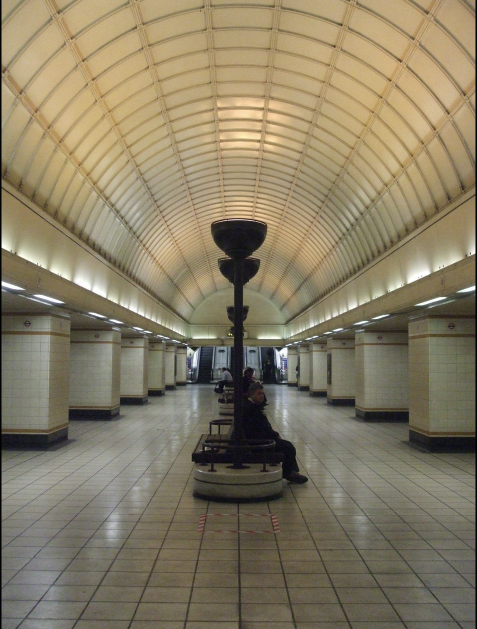

In 1937, one year after Gillian Wise was born, construction on the Gants Hill underground station in Ilford began. The station was designed by Charles Holden and was inspired by stations on the Moscow Metro.
Before it was eventually opened to the public in 1947, the ‘under construction’ station was used as an air-raid shelter. After consultation between Moscow and London about the building of the Moscow Metro in the 1930s, British architects returned to London with some new ideas. Gants Hill is designed with a central vaulted concourse separating two platforms in order to maximise the amount of space for the flow of people.
Getting to the platform level of the station is a striking experience. As you travel down the deeply-set downward steps the square floor tiles slowly come into view before the marvel of the ceiling is revealed. The station has barrel-vaulted ceilings and is tiled in a geometric pattern that is reminiscent of the Krasnye Vorota Metro station in Moscow which opened in 1935.
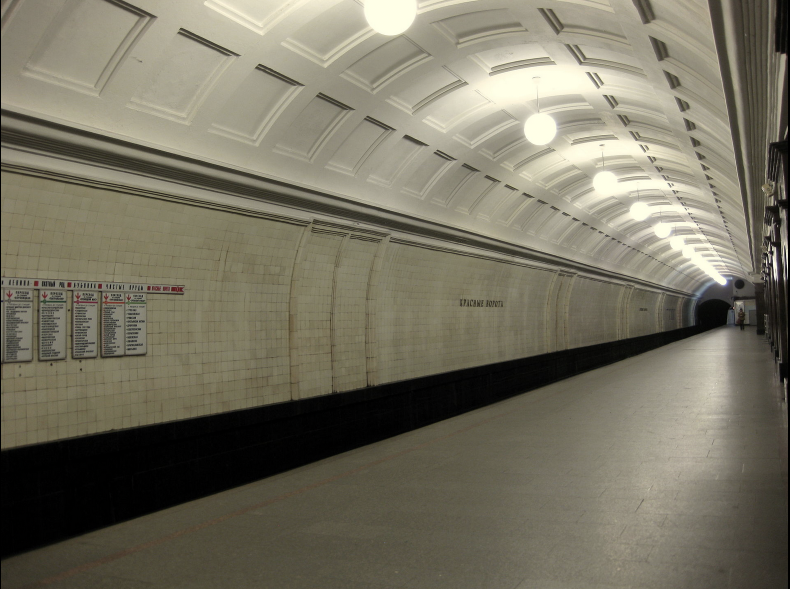

Ivan Fomin was the designer of the Krasnye Vorota Metro Station. Fomin worked in a variety of styles throughout his lifetime, including Art Nouveau, Neoclassicism and an intermediary style of architecture known as Postconstructivism.
By the early 1930s, Constructivist art and architecture had fallen out of favour and was soon to be replaced. Stalinist architecture would become the dominant form of expression for the next decades. Wedged in between these two larger forms is a brief architectural style known as Postconstructivism (sometimes referred to as early Stalinism).
Constructivist work had been wildly imaginative and avant-garde in its use of shapes, materials and technology. It was avowedly political, aiming to incite a social purpose for all people in public spaces. The demise of Constructivism comes alongside the rise of Stalin and the impact of centralised state power. The Stalinist architecture that followed utilized classical forms representing a return to traditional notions of power. Dmitry Khmelnitsky writing about this period suggested that Constructivism was ended by the force of Stalinist power. Khmelnitsky suggests that “traces of the Constructivist style in the Postconstructivism of the 1930s are a sign of indecision, not tradition.” There was a vacuum that state-sponsored artists were filling with a combination of what came before (Constructvisim) and even further back (Classicicism). This combination of ideas was the starting point for Stalinist architecture. Postconstructivism is truly then a misnomer for the return of classicist forms and styles with accidental traces of Constructivism.
Ivan Fomin himself had a deep love for classicism and had spent a long time attempting to develop his own form of proletarian classcisim. In the 1930s he partook in key competitions to design the Moscow Metro. He won just one and designed the station Krasnye Vorota with vaulted ceilings and a central concourse. A model of the station was at the 1938 World’s Fair in Paris where it won the Grand Prix. Fomin designed the station in what would become called Postconstructivism.
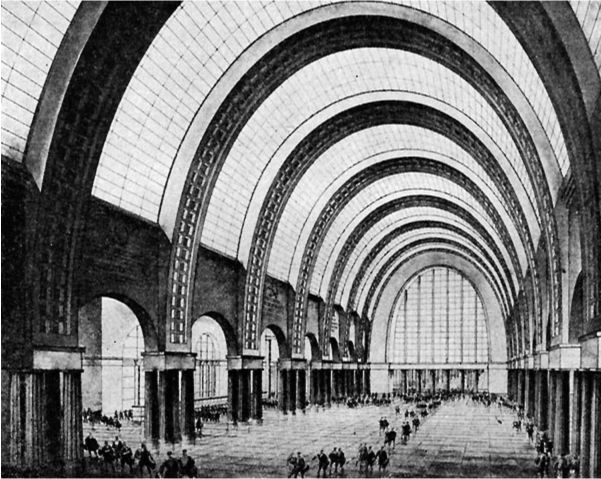

Gants Hill station in Ilford, designed by Charles Holden adapted from a design by Ivan Fomin, bares the scars of the Constructivist movement being clamped down on by the Stalinist regime.
Gillian Wise, born in Ilford, developed a career as an artist inspired by Russian constructivist art. She would even travel on a British government grant to research Russian constructivism in the country itself.
Only after this trip to Russia does Wise give up being a Constructivist artist and move on to join the Systems group.
I’m not saying that architectural ghosts haunted Gillian Wise as a child until she was able to exorcise them in the country from which they originated but…I am saying that.